CLASS - XI, UNIT-2 NETWORKING AND INTERNET, I,T-SKILLS-802
UNIT-2
NETWORKING AND INTERNET
Important Q/ ANS
|
1.
ARPANET:
Advanced Research Projects Agency Network
2.
LAN: Local area network
3.
MAN: Metropolitan area network
4.
WAN: Wide-area network
5.
WWW: World Wide Web
6.
TELNET: Teletype Network.
7.
PSTN:
Public Switched Telephone Network
8.
TCP/IP:
Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol
9.
IETF:
Internet Engineering Task Force
10 ICANN: Internet Corporation
for Assigned Names and Numbers
11 NIC:
Network Interface Card
Q2: What is communication?
Communication
is the process of sharing information, ideas, thoughts, and feelings between
two or more people. It is a two-way process, involving a sender and a receiver.
Q3: What are the elements of communication?
The
key elements of communication:
- Sender: The person who initiates the communication
process.
- Receiver: The person who receives the communication
message.
- Message: The information that is being shared.
- Channel: The medium through which the message is sent.
- Feedback: The response from the receiver to the message.
Q4: What are the three modes to transmit data in a communication
network?
Three
modes of transmission are simplex, half-duplex, and full-duplex.
In
simplex mode, information can be transferred only in one direction. This mode
is termed unidirectional. E.g.: Radio, satellites are simple in nature.
In Half-duplex mode is a
bidirectional communication between the two nodes, however, only one node at a
time can transmit the data. E.g.: Walkie-Talkie.
In full-duplex mode both
communicating parties can send and receive at the same time. E.g. Voice Call,
Video call
Q5: What is computer network?
A
collection of interconnected nodes which communicate by means of some channel
form a computer network.
Q6: What are the uses of computer network?
1. 1. Resource sharing: Computer
networks allow users to share resources such as printers, scanners, and
software
- Improved communication: Computer
networks can help to improve communication between people and
organisations. Through email, video conferencing, and other collaboration
tools.
- Increased productivity: Computer
networks can help to increase productivity by allowing users to access
information and resources more quickly and easily.
- Reduced costs: Computer
networks can help to reduce costs by eliminating the need for duplicate
resources.
- Global reach: Computer
networks can provide global reach, allowing users to connect with people
and resources all over the world.
- Data Backup:
Computer networks can be used to back up data and applications.
Q7: Define Transmission medium and its types?
A transmission medium/ communication channel is
a physical path or substance that allows signals to be transmitted from one
point to another.
Guided Medium: It means physical conductors such as
twisted pairs, coaxial cable, and fibre optics.
Unguided Medium: It uses electro-magnetic waves that
do not require a physical conductor
Guided Medium
1.
Twisted
pair cables: These are the most common type of guided transmission media. They are
made up of two insulated copper wires twisted together.
2. Coaxial
cables: These cables consist of a central copper core surrounded by a layer of
insulation, which is then wrapped in a metal shield.
3.
Fibre
optic cables: These cables consist of a core of glass or plastic surrounded by a
cladding layer. The core and cladding have different refractive indices, which
allows light to be guided along the cable.
Unguided Medium
1.
Radio
waves: These waves are used for long-distance communication. They can travel
through the air, water, and even through solid objects.
2.
Microwaves:
These waves are used for short-range communication. They can travel through the
air, but they are blocked by solid objects.
3.
Infrared
waves: It’s a type of electromagnetic radiation that has wavelengths longer
than visible light but shorter than radio waves. They are invisible to the
human eye, but they can be felt as heat. E.g. Remote controls use infrared
waves to send signals to devices such as TVs and stereos.
Q7: Define Network Devices?
A network device is a physical or software
component that enables computers, printers, and other devices to connect to a
network and communicate with each other. They are responsible for routing data
packets, managing traffic, and providing security.
E.g. Repeater, hub, router, bridge, switch and
gateway
Q8: What is the purpose of network devices? Explain following
network devices.
Repeater, Hub, Router, Bridge, Switch and
Gateway
Repeater:
1. A repeater is
used to restore the input signal to its original form, so that it can travel a
larger distance.
2. A repeater is an electronic device that receives a signal and
retransmits it.
3. It is used to extend the range of a signal by amplifying it.
4. A repeater is
used to restore the input signal to its original form, so that it can travel a
larger distance.
5.
It is also known as digital generator
|
|
1.
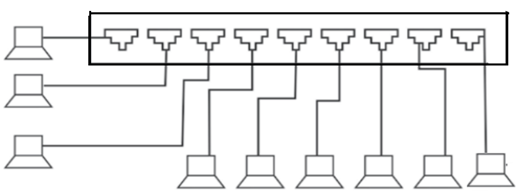
A hub
is a network device that connects multiple devices together on a single network
segment.
2.
A hub comprises several input/output
(I/O) ports
3.
Data arriving on an incoming line is
output to all lines except the line on which the hub receives the data.
|
|
1.
Switches
are a more intelligent and efficient way to connect multiple devices together
than hubs.
2.
Unlike bridges, which connect two or
more LAN segments, switches, are used to connect individual nodes in the
network with each other.
3.
They
are also more secure.
|
|
Router:
1.
Determines
the best route for the data packets to travel to their destination
2.
Routers
also provide security features
3.
A router transmits data from incoming
network to another network.
4.
A router maintains a routing table of
various networks.
|
|
A
bridge is a multi-port device used for connecting two or more local area
networks (LAN), possibly operating at different speeds.
Unlike
hubs, they are intelligent devices, which exercise discretion while forwarding
data.
A gateway is a network device that connects two
or more networks together.
It is used to translate data from one network
protocol to another, so that devices on the different networks can communicate
with each other.
1.
LAN,
MAN, WAN
2.
Internet
and WWW
3.
Email
and Chat
4.
Firewall
and Antivirus
|
Network |
LAN |
MAN |
WAN |
|
Full Form |
Local Area Network |
Metropolitan Area Network |
Wide Area Network |
|
Geographic
scope |
Small
area |
City
or metropolitan area |
Large
geographic area |
|
Ownership |
Single
organisation |
Public
or private organisation |
Telecommunications
company |
|
Purpose |
Connecting
computers and devices within a single organisation |
Connecting
LANs within a city or metropolitan area |
Connecting
LANs and MANs over a large geographic area |
|
Speed |
High |
Moderate |
Low |
|
Latency |
Low |
Moderate |
High |
|
Cost |
Low |
Moderate |
High |
b.
|
Internet |
WWW |
|
A
global network of computers |
A
system of interlinked hypertext documents |
|
To
connect computers and allow them to communicate with each other |
To
provide a way to access information on the internet |
|
TCP/IP
protocol |
HTTP
protocol |
|
Email,
file sharing, video conferencing |
Websites,
web browsers, search engines |
c.
d.
|
Firewall |
Antivirus |
|
To
protect your computer or network from unauthorised access |
To
protect your computer from viruses, malware, and other malicious software |
|
Monitors
and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic |
Scans
your computer for viruses, malware, and other malicious software |
|
Hardware
firewalls, software firewalls |
Behaviour-based
antivirus |
|
Protects
your computer or network from unauthorised access |
Protects
your computer from viruses, malware, and other malicious software |
|
|
Q10. What are cookies?
Cookies are small text files that a website
saves on your computer or mobile device when you visit the site. They are used
to remember your preferences, such as your language, font size, and other
display preferences. They can also be used to track your browsing activity
across different websites.
Q11. Define the following:
1.
Protocol
2. Cyber crime
3.
Cyber
law
4.
Digital
Literacy
Protocol: A protocol is a set of rules that define how
data is formatted, transmitted, and received between devices on a network.
Cyber-crimes: Cyber-crimes are the crimes related to
the misuse of computers or the internet such as theft, fraud, forgery. E.g. Phishing, Malware, Cyber-bullying and Identity theft. Cyber-crime
as an unlawful act where in the computer is either a tool or a target or both.
Cyber law: Cyber law is a broad term that refers to the legal issues
related to the use of computers and the internet. E.g. Intellectual
property: Cyber law deals with the protection of intellectual property
rights in the digital age, such as copyright, trademark, and patent law.
Digital Literacy: Digital literacy
refers to raising knowledge and awareness about technology such as desktop
computers, smartphones, tablets, and other electronic gadgets. It also includes
familiarity with software tools and the internet.
Q12. Explain TCP/IP Model.
The
TCP/IP is the glue which holds the internet and WWW together .A set of communication protocols allows computers to connect
to each other and exchange data over the internet. It
is divided into four layers:
- Physical
layer
- Data link layer
- Network
layer
- Transport layer
Q13. List various protective measures
that can be taken for network security.
1.
Never click on a suspicious link.
2.
Make sure that passwords are strong
and are changed frequently.
3. Never disclose personal information
such as date of birth, account details, passwords, credit and debit card
details.
4.
Do not post any offensive content on
social networking site.
5.
Use updated antivirus and firewall.
Network topology is the arrangement of the
elements (links, nodes, etc.) of a communication network.
1. In bus topology, there is a long
cable, called backbone cable (or simply backbone), that connects various nodes
through a connector called tap.
2.
In ring topology, all the devices are
attached through a cable in the form of a ring.
3.
In star topology, all the devices are
connected to the central controller called hub.
4.
In mesh topology, all nodes are
connected with every other node in the network.
5.
In Tree topology is a combination of
star and bus topology.
Q15. Write a short note on the following:
1.
TELNET
2.
FTP
3.
DNS
TELNET: Telnet stands for terminal network.
It is a client server-based application that allows the user working on one
system to login and access a remote system
FTP: FTP is a File transfer Protocol used for
transferring files from one machine to another
DNS: The
Domain Name System (DNS) is a hierarchical naming system for computers,
services, or any resource connected to the Internet or a private network.
Q16. Write a short note on Following
MAC Address
IP Address
Every machine in a network has another unique identifying number, called its IP Address. An IP address is a group of four bytes (or 32 bits) each of which can be a number from 0 to 255. A typical IP address looks like this: 59.177.134.72
Q17. Explain Domain Name system
It is practically impossible for a person to remember the IP addresses of all the computers one may have to communicate with. Therefore, a system has been developed which assigns names to some computers (web servers) and maintains a database. These names are called Domain Names. Examples: cbse.nic.in
Generic Domain Names:
·com - commercial business
·edu - Educational institutions
·gov - Government agencies
·mil - Military
·net - Network organizations
·org - Organizations (nonprofit)
Country Specific Domain Names:
.in - India
·au - Australia ·ca - Canada
.us - United States of America
Q18. What do you mean by Network Security Tools and Services?
1. Firewalls
- What It Does: Blocks unwanted internet traffic to protect your computer.
- Like: A security guard at the entrance of your house.
2. Antivirus Software
- What It Does: Detects and removes harmful software from your computer.
- Like: A medicine that cures your computer from infections.
3. Password Managers
- What It Does: Stores and manages your passwords securely.
- Like: A secure vault where you keep all your keys (passwords) safe and organized.
4.Cyber Law Cyber laws are the laws for systematic use of e-resources, for example, e-business, and serve as a measure against illegal cyber-crime. Various cyber laws have also been enacted to prevent cyber-crimes
Q19. List some Protective Measures while accessing Internet for staying safe while using the internet.
Use Strong Passwords:
- What to Do: Make passwords long and mix letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Why: Harder for hackers to guess.
Keep Your Software Updated:
- What to Do: Update your apps and operating system regularly.
- Why: Fixes security holes and keeps you safe.
Be Careful with Links:
- What to Do: Don’t click on suspicious links in emails or messages.
- Why: Protects you from scams and malware.
Share Personal Info Wisely:
- What to Do: Only give out personal details to trusted sites.
- Why: Keeps your private information safe.
Install Antivirus Software:
- What to Do: Use software that scans for and removes viruses.
- Why: Protects your computer from harmful programs.
Secure Your Wi-Fi:
- What to Do: Set a strong password for your home Wi-Fi.
- Why: Prevents others from accessing your network.
Back Up Your Data:
- What to Do: Save copies of important files in a separate location.
- Why: Protects your data in case of loss or damage.
Avoid Public Wi-Fi for Sensitive Activities:
- What to Do: Don’t use public Wi-Fi for online banking or shopping.
- Why: Public networks are less secure.
Q20. Mention Some Cybercrime and Cyber Threats.
Cyber bullying Harassment or bullying inflicted through the use of electronic or communication devices such as computer, mobile phone, laptop, etc.
Cyber stalking Use of electronic communication by a person to follow a person or attempts to contact a person to foster personal interaction repeatedly despite a clear indication of disinterest by such person.
Online Job Fraud An attempt to defraud people who need employment by giving them a false hope/ promise of better employment with higher wages.
Vishing To seek personal information like Customer ID, Net Banking password, ATM PIN, OTP, Card expiry date, CVV etc. through a phone call.
SMSing Use of mobile phone text messages to lure victims into calling back on a fraudulent phone number, visiting fraudulent websites or downloading malicious content via phone or web.
SIM Swap Scam Getting a new SIM card against a registered mobile number
Credit card (or debit card) fraud an unauthorized use of another's credit or debit card information for the purpose of purchases or withdrawing funds from it.
Identity theft Dishonestly making use of the electronic signature, password or any other unique identification feature of any other person.
Spamming Persuading a recipient to buy a product or service, or visit a website via email, SMS, MMS where he can make purchases.
Ransomware The victim is asked to pay the demanded ransom to get his device decrypt






Comments
Post a Comment